
Top 10 Most Dangerous Viruses in the World in 2023
Navigating the Microbial Minefield: A Brief Overview of the Global Health Landscape
As the year 2023 concludes, the global community remains confronted with a multitude of health concerns, among which the enduring menace of perilous infections remains. This article will examine the ten most perilous pathogens that present a substantial threat to the well-being of the entire world. Regarding their origins and effects on human populations, every virus possesses a unique narrative. We shall explore the realm of infectious maladies in order to comprehend the perils they may pose.
READ ALSO: 10 Most Dangerous Cities In Oklahoma 2023: Crime Statistics And Safety Concerns In Oklahoma
- HIV/AIDS (Human Immunodeficiency Virus / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome):
- Description: Despite decades of research and advancements in treatment, HIV/AIDS remains a formidable foe. The virus attacks the immune system, leaving individuals susceptible to other infections and diseases.
- Fatality Rate: Although the fatality rate has decreased with improved treatments, HIV/AIDS continues to claim lives, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare.
- Ebola Virus:
- Description: Originating from Africa, the Ebola virus causes severe hemorrhagic fever with a high mortality rate. Transmission occurs through contact with infected bodily fluids.
- Fatality Rate: The fatality rate can be as high as 90%, making Ebola one of the deadliest viruses known to humanity.
- SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2):
- Description: Responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, SARS-CoV-2 is a highly contagious respiratory virus. It can cause severe respiratory illness and has led to millions of deaths worldwide.
- Fatality Rate: The fatality rate varies, with higher risks for older adults and those with underlying health conditions.
- Hantavirus:
- Description: Transmitted by rodents, hantaviruses can cause hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) in humans, leading to severe respiratory distress.
- Fatality Rate: HPS can have a mortality rate ranging from 30% to 50%, depending on the specific strain of the virus.
- Marburg Virus:
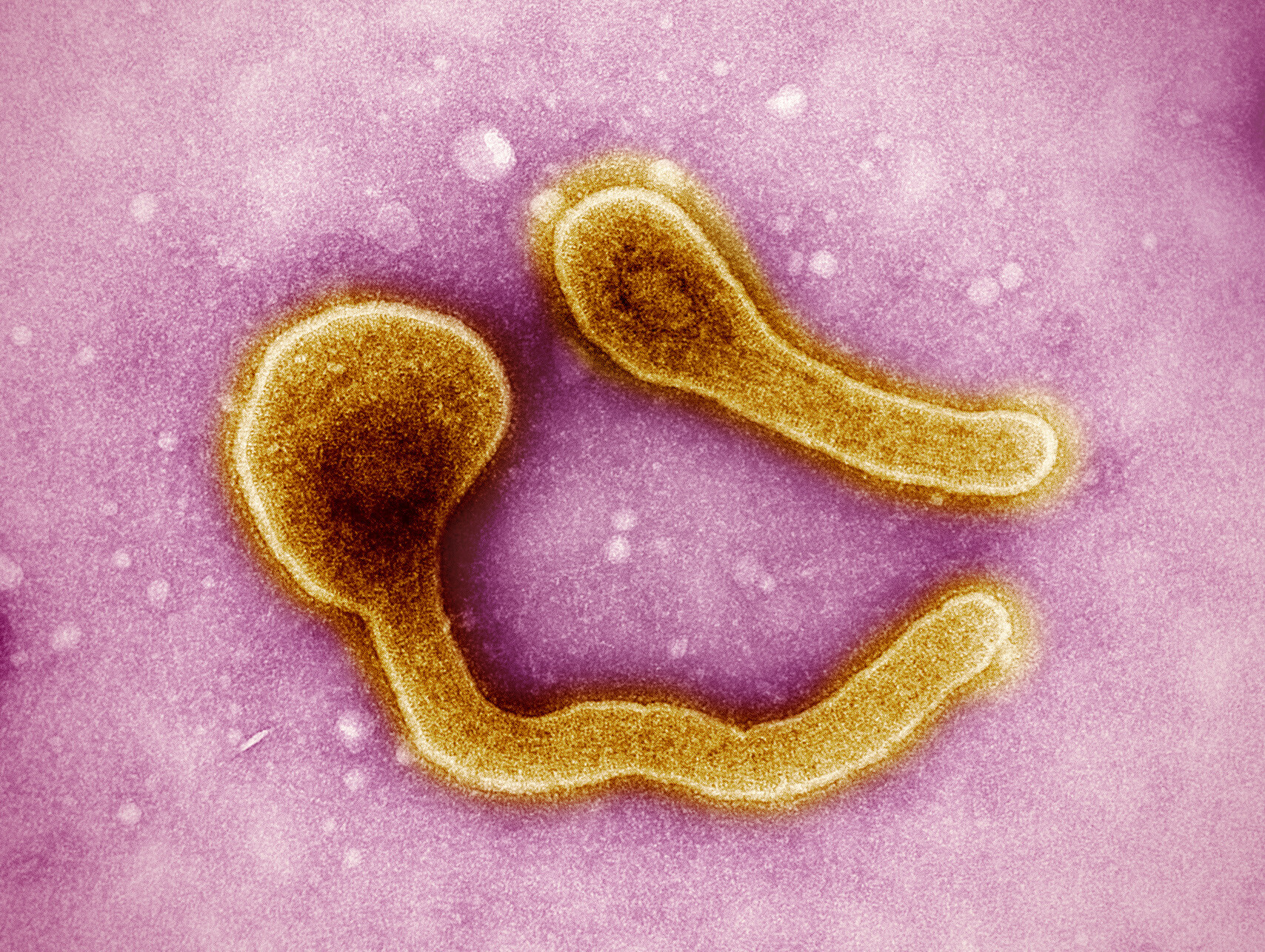
- Description: Similar to Ebola, the Marburg virus causes hemorrhagic fever with a high fatality rate. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with the blood, secretions, or organs of infected individuals.
- Fatality Rate: Marburg virus infections have historically had mortality rates exceeding 80%.
- Rabies Virus:
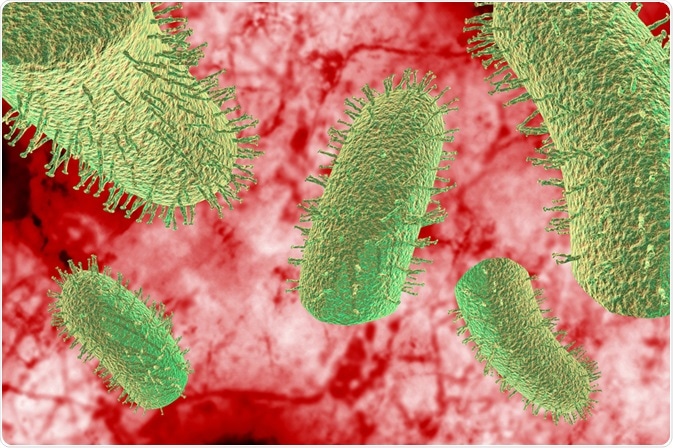
- Description: Typically transmitted through bites from infected animals, rabies attacks the central nervous system, leading to neurological symptoms and death if not treated promptly.
- Fatality Rate: Once clinical symptoms appear, rabies is almost universally fatal, with a fatality rate close to 100%.
- Lassa Fever Virus:
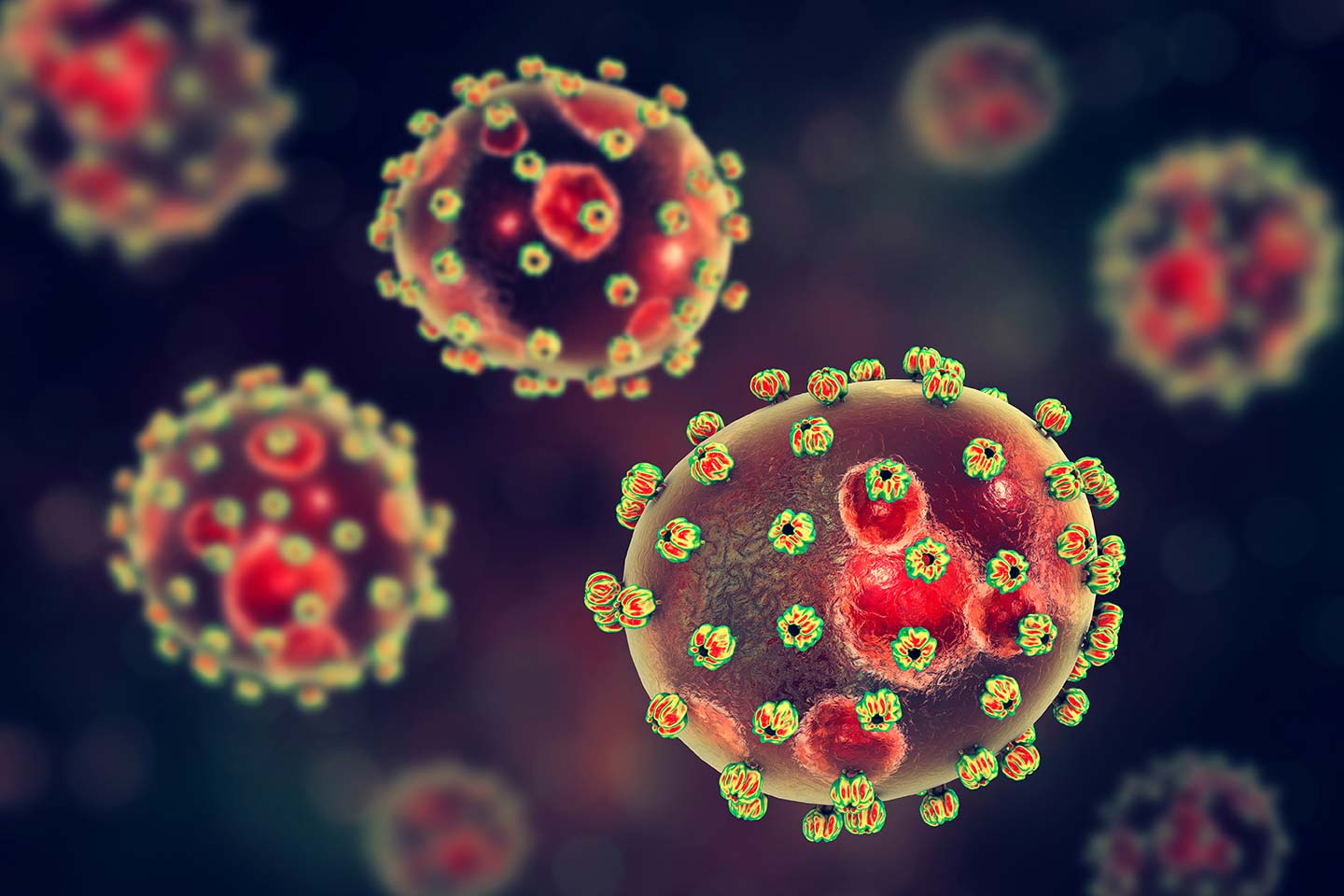
- Description: Endemic in West Africa, Lassa fever is a viral hemorrhagic fever with rodent-to-human transmission. It can lead to severe multi-organ failure.
- Fatality Rate: While the overall fatality rate is around 1%, it can rise to 15% in severe cases.
- Nipah Virus:
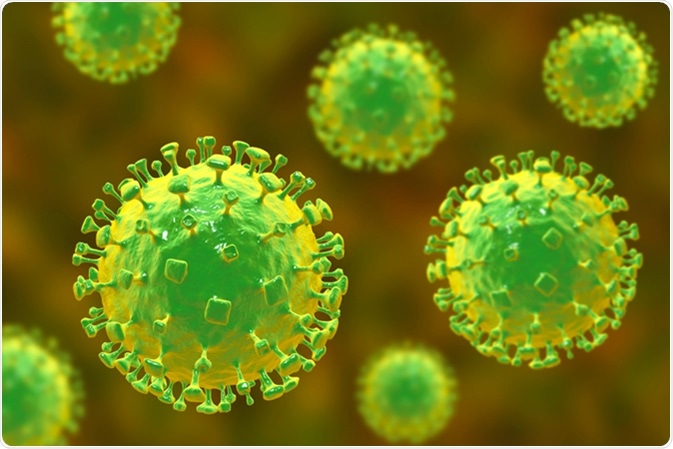
- Description: Nipah virus, transmitted from bats to humans, can cause severe respiratory and neurological symptoms.
- Fatality Rate: The fatality rate for Nipah virus infections can range from 40% to 75%, depending on the outbreak and healthcare infrastructure.
- MERS-CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus):
- Description: Similar to SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV causes respiratory illness, with camels believed to be the primary source of infection in humans.
- Fatality Rate: MERS-CoV has a higher fatality rate than SARS, approaching 35%.
- Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever (CCHF) Virus:
- Description: Tick-borne, CCHF virus causes severe hemorrhagic fever, with symptoms ranging from mild to life-threatening.
- Fatality Rate: The fatality rate for CCHF virus infections can be as high as 40%, making it a significant concern in affected regions.
These 10 viruses highlight the ongoing challenges faced by global healthcare systems. Understanding their characteristics, transmission patterns, and fatality rates is crucial in developing effective preventive measures, treatments, and responses to emerging viral threats. As we move forward, continued research, international collaboration, and advancements in public health infrastructure are essential to combatting these dangerous viruses and safeguarding global well-being.
READ ALSO: 10-Point Overview Of Neighborhoods In Los Angeles With High Crime Rates And High Resilience

















































